The world around us is changing rapidly due to technological advances. But which developments are having the biggest impact?
In my work as technology futurist, futurologist and innovation-expert, it is important to follow (technological) trends and developments. In this article you will read a comprehensive overview, including examples, benefits and caveats.
- Are you curious about the (technological) trends each year? Then read among others: These are the (technological) trends of 2025, 2024, 2023, 2022, and 2021.
Structure of this article
In this article, you will first read more about technological developments. Then you will read more about some modern developments. Finally, as an extra you will learn more about characteristics of technological development, such as exponential change. At the end you will find a list of more resources, such as interviews, podcasts, and videos.
If you would like to hire me for a lecture or workshop on (technological) trends, please contact me. Or check out the Trends 2040 page first for more information, examples and references.
Technological developments
I think this is (currently) the most important technological developments in the coming years:
- Artificial intelligence and robots
- Mobility: self-driving cars, flying cars and drones
- Virtual reality and the metaverse
- Blockchain and cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin
- Quantum Computing
- Energy transition, including nuclear fusion
- Biotechnology and synthetic biology
I have elaborated on these developments below. I have written a separate article about some developments. Of these you can click the link to read further.
Development 1: Artificial intelligence and robots
Artificial intelligence
One of the biggest technological developments today and for the future is artificial intelligence. The definition: non biological systems that are self-learning. They learn independently in different ways, depending on the extent to which humans still guide the algorithm (or completely let go after giving it some parameters).
This is related to big data: using data from apps, sensors and (Internet) platform about the status of parts or people’s behavior.
Robots
What are robots? We know robots mostly from movies. I always picture a square metal thing that talks tinny and moves woodenly. But really, robots are just the shell of artificial intelligence. A robot can take many forms. In essence, a robot is programmed to perform various tasks.
The definition of a robot is a machine that can perceive, think and act. A camera (perceiving) is not a robot; the elements must be interrelated. Examples include a welding robot in a factory, robots used in healthcare (for example, for lifting patients) or robots at the airport (helping travelers with their flight information).
As with drones, robots by themselves are not very exciting. What matters is the combination of this trend with other trends. Can we use robots to help us in our sustainable energy supply, put them inside our bodies or send them into space to mine resources?
Development 2: mobility, such as self-driving cars, flying cars and drones.
Mobility
A while ago I spoke to Professor Carlo van Weijer (Eindhoven University of Technology). A nice anecdote he shared is Marchetti’s Constant. Van der Weijer:
In recent decades, we have been traveling an average of 1 hour and 6 minutes per day, despite the increased speed at which we travel. Average travel time remains the same despite the fact that we have gone from horse-drawn carriages to cars and airplanes.
What will it be like soon with self-driving cars?
Self-driving cars
Currently, 1.2 million people die in and from traffic each year. This figure went down for a very long time, but has been increasing again in recent years. This is probably due to the introduction of the smartphone, where drivers are not paying attention to the road.
Cars that drive themselves using artificial intelligence will save a lot of traffic deaths. According to Neil Jacobstein (chair of artificial intelligence at Singularity University), that’s the striking thing, too. Jacobstein:
‘Everyone is talking about the fatal accident involving a self-driving Tesla. No one is talking about the 1.2 million traffic fatalities a year because we humans drive ourselves.’
Carlo van der Weijer expects self-driving cars to be inevitable. Our view of mobility will also change in the process. The days of owning a car will also become obsolete at some point.
Mobility is becoming a service. In a sense, this trend has already begun with companies such as Uber and SnappCar. This also has an impact on the government. It will no longer invest in buses or trains, but in a network of self-driving electric cars.
Flying cars
An outing are flying cars. I expect it will be more of a gimmick than cars that drive autonomously. Still, there are a number of technology companies working on this, such as:
- Joby Aviation (USA)
- Archer Aviation (USA)
- Volocopter (Germany)
- Ehang (China)
Experts expect that in the long run a VTOL (Vertical Take-Off and Landing) is easier and safer than cars that have only the ground to move across (and thus cannot go up and down).
Drones
From flying cars, it’s a small step to drones. The technology itself is not at all new or exciting. Drones are used in the military and by consumers as well.
The definition of “drone” is that it is a pilotless aircraft. The word drone comes from the English word for male bee (dar). Drones are controlled remotely. Sometimes with a joystick, while you continue to see the drone, and sometimes remotely with camera images and other sensor data.
Development 3: virtual reality and the metaverse.
Virtual reality
Virtual Reality artificially recreates sensory experiences in terms of sight, sound and touch. The applications currently on the market still focus mainly on images and vision. You can use a VR to look completely (360 degrees) around you at a virtual world. In VR, images are created via a special kind of software, which are then displayed in glasses.
Augmented reality actually uses the same technology as virtual reality, only with the difference that you can still see the real environment. For example, with augmented reality you can see the room, but you can also see a miniature race track in the room. It’s kind of like a hologram. Or a digital layer in reality.
Metaverse
In October 2021, the term metaverse became common knowledge. That’s when Mark Zuckerberg announced that the parent company of Facebook, Whatsapp, Oculus and Instagram was renamed Meta.
In an article on Medium, Aaron Frank provides a clear definition:
The Metaverse is the Internet, as well as a spatial (and often 3D), game-engine-powered collection of virtual environments.
From then on, programmers built these virtual worlds, funded with huge sums of money. For example, Meta puts $10 billion a year into the development of the Metaverse. After the stormy rise of Large Language Models, such as ChatGPT, Meta incidentally put its investments in these virtual worlds on hold.
In the coming years, I am especially curious to see how we as humans shape the Metaverse and how it will shape us. Do we prefer a virtual world to this one? What does it mean for our relationship with our bodies?
Development 4: blockchain and cryptocurrencies, such as bitcoin.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology allows you to enable transactions between people who do not know or trust each other, without the need for a central party (intermediary or middleman). This is because the database is shared online. Anyone can copy, edit and store the ledger. The database is not intended to store large amounts of information. Any change in the ledger is recorded – these are mutations or transactions.
The nodes in the network check whether the changes comply with predefined game rules. When new requests arrive and if they are approved, it is immediately distributed to all blockchain participants.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a digital currency. Another word for digital currency is cryptocurrency. In the fall of 2016, there were about 700 digital currencies. By early 2021, there will be more than 900. Bitcoin is the largest, with a financial size of 80%. Ethereum is the 2nd largest currency.
Often, bitcoin is confused with blockchain. Bitcoin is actually the currency, while blockchain is the technology behind it.
Development 5: quantum computing
Quantum computing
A brief description of quantum computing: in ordinary computers, transistors switch on or off to symbolize ones and zeros. Quantum computers use quantum bits, also called qubits. This all takes place on a different scale than we are used to: at the level of atomic and subatomic physics, with atoms, electrons and other miniscule particles.
Because of the special properties of quantum physics, these qubits can exist in superposition. Here, the bit is both a 0 and a 1. By connecting multiple qubits in a computer, the computational power grows exponentially.
Quantum signals
Currently, quantum computers are still under development. In terms of performance, they are nowhere near the level of ordinary computers. Still, I find it a fascinating field. It will be some time before we can use the power of quantum, where we probably won’t have quantum computers on our desk. It will probably be more of a service, just as we use electricity now.
These are some interesting signs about quantum computing and networks:
- There are still relatively few programmers who can handle quantum computing. This hinders the further development of this field. To address this, IBM published a tutorial for beginners in 2022. This allows you to build quantum algorithms and test them on IBM’s quantum computer available in the cloud.
- Whereas Europe has missed the battle (for now) with artificial intelligence and synthetic biology, it is different in the field of quantum computing. One reason is that Europe, particularly Germany, was at the forefront of quantum physics. This began in 1900 with the publication of German physicist Max Planck’s groundbreaking formula on thermal radiation.
- Experts estimate the current market size of quantum computing in Europe at 500 million euros. The European Union, governments and an increasing number of private organizations are investing in promising start-ups. Examples include Finland’s IQM working on solutions around climate change, France’s Pasqal and England’s Oxford Quantum Circuits.
Willow chip from Google
In late 2024, Google announced the performance of its quantum Willow chip. This chip does a calculation in 5 minutes that would take the world’s fastest supercomputer 10 septillion years. That’s a 1 with 25 zeros. This is older than the age of the universe.
By the way, it’s not about who is the fastest. The real news is that Google is demonstrating that their quantum computer gets better and better as you put more processing power into it. The more power, the more accurate it works.
Hartmut Neven, head of Google Quantum AI, says: ‘The more qubits we add, the fewer errors the system makes. That’s crucial for building quantum computers that are really useful.’
Development 6: the energy transition.
Energy Transition
In the fall of 2016, I was at the Singularity University the Netherlands Summit in Amsterdam. There, Ramez Naam talked about the energy issue. He is not at all pessimistic about climate change. He believes in sustainable energy generation. In fact, in his presentation he gave examples that developments in this area are moving at lightning speed.
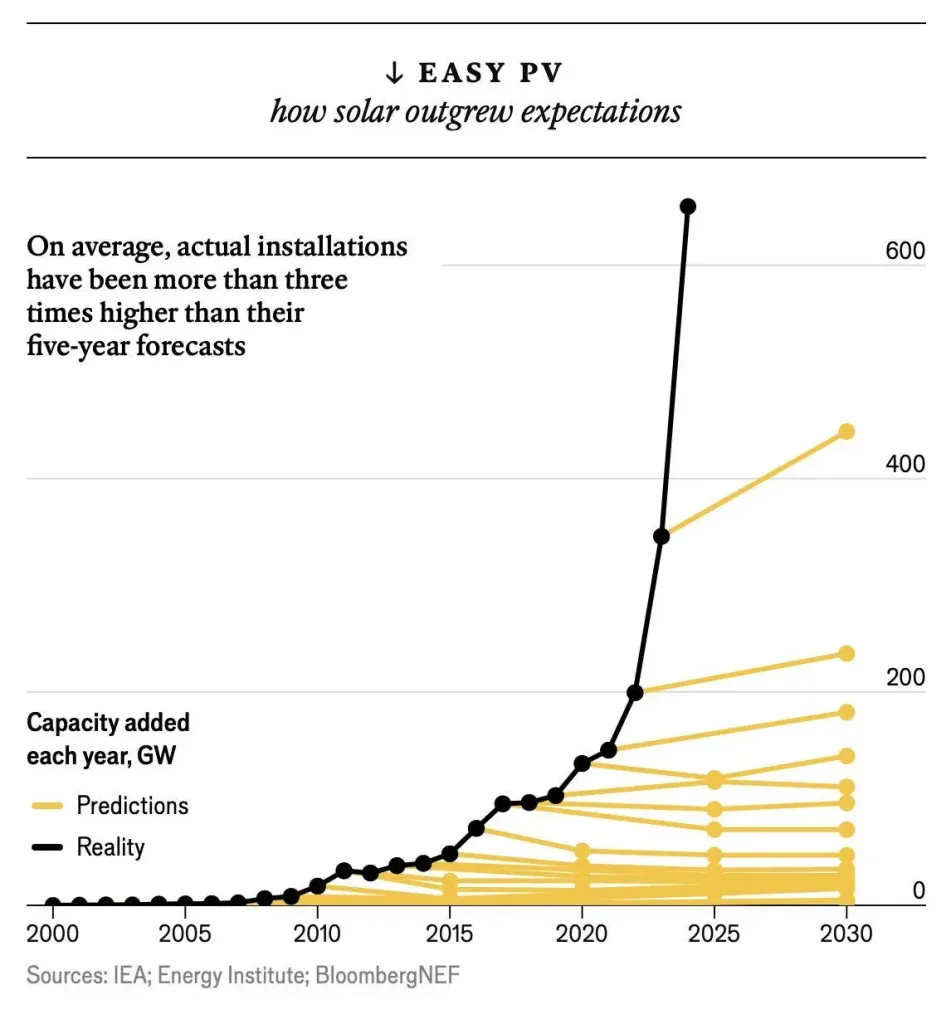
In some countries, solar energy was already cheaper than energy from coal-fired power plants in 2017. The share of renewable energy generation relative to total energy generation has grown 100 times over the past 13 years.
This is exponential growth. His vision: ‘The price of solar power is going to almost zero. The storage capacity of batteries is going up radically.’
The price of solar goes to almost zero
Ramez Name
Growth capacity
Naam’s prediction seems to be coming true. Every year for the past decade, the International Energy Agency (IEA) has had to revise upward its predictions about solar energy. And not by much. Actual solar installations turned out to be as much as three times more numerous than what the agency had predicted five years ago.
The main reason is that renewable energy sources such as solar collectors are a technology, rather than a resource such as coal, oil and gas. A characteristic of technology is that it can become (exponentially) better, faster and cheaper.
Other forms
Besides energy from solar collectors and wind turbines, there are other promising forms of energy generation:
- Nuclear Fusion
- Geothermal
Nuclear Fusion
There are two forms of nuclear reactions: fission and fusion. Fission is the method used in nuclear reactors. In this process, large radioactive nuclei are split into smaller isotopes (neutrons) or elements (protons).
Nuclear fusion is precisely about combining small nuclei into heavier elements. Such as bringing together two hydrogen atoms with one proton each to a helium atom with two protons. This fusion reaction also occurs on the sun, for example, through a combination of extreme temperatures and high pressure.
In recent decades, much research has been done on nuclear fusion. What makes nuclear fusion especially difficult is getting the repulsive nuclei to fuse under extremely high temperatures. Still, governments and scientists are putting a lot of time and money into it because the potential is huge. After all, if nuclear fusion succeeds, it is an inexhaustible fuel, with no long-lived radioactive waste and no risk of nuclear meltdown.
A few recent breakthroughs:
- In 2024, the world’s largest experimental nuclear fusion reactor was announced to have generated a record amount of energy. The European fusion experiment Joint European Torus (JET) produced 69.26 megajoules of heat energy in 5.2 seconds in October 2023. That is comparable to the electrical energy consumption of a three-person household in two days. To do this, the reactor used only 0.21 milligrams of fuel, the weight of a fruit fly.
- SPARC will open in late 2025. This machine is built by Commonwealth Fusion, a spinn-off of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in the United States. SPARC will eventually generate 140 megawatts.
Geothermal
Geothermal energy is on the verge of a breakthrough in 2024(source). Take the company Fervo Energy. Fervo applies fracking techniques to extract heat from the subsurface. With new techniques, companies hope to start generating more than 5,500 gigawatts of energy in the United States.
Development 7: biotechnology and synthetic biology.
Biotechnology
Personally, I find the huge increase in computing power and memory storage represented by Moore’s Law incredibly interesting, but I find even more fascinating the advances in biotechnology.
For example, one of the drivers in advances in biotechnology is the declining cost of analyzing DNA. This decline is faster than Moore’s Law. An article in The Economist in 2006 referred to this as the “Carlson Curve,” after the author of the piece. The assumption was that the cost of “DNA sequencing” would keep pace with Moore’s Law, but in 2008 it appeared to be going even faster.
Related to biotechnology is synthetic biology: the (re)design and replication of cells, parts or groups of cells that make up an organism.
Store data
One particular application of biotechnology is data storage. Through social media, sensors and artificial intelligence, we are producing more and more data.
A solution to the storage problem may lie in biology. This is called “biomimicry. In fact, nature has already found a solution for data storage. That is DNA. DNA is compact, it can last hundreds of thousands of years, it can withstand extreme cold or heat, you can make millions of copies per hour, and we can code it easily.
According to Yaniv Erlich (Columbia University), DNA does not lose its storage quality with age. Something that does happen with cassette tapes, CDs and hard drives. Scientists have already done the first successful experiments with this, such as encoding and sending a sonnet by Shakespeare via DNA.

What are other more unusual modern developments?
Modern developments
In addition to the developments in the previous section, here are other exciting technology trends:
- Materials Science
- 3D printing
- Space
1. Materials Science
Materials science drives other developments. With better, stronger and smarter materials, we can make better sensors or conductive components, for example. These are interesting materials:
- graphene
- borophene
Graphene
It is transparent. It is stronger than steel. It is super conductive, ductile and the thinnest material in the world. In recent years, more and more is becoming known about graphene. In 2010, the Nobel Prize in Physics was even awarded to the discoverers and developers of this material.
So what is it? Graphene is made of carbon. When you write with a pencil, you are actually working with graphene. Because graphene is in graphite, which is what your pencil tip is made of. The special thing about graphene is that it is only one atom thick. Such a thin slice is called two-dimensional material.
What distinguishes graphene from other two-dimensional materials is that graphene is strong and stable. It is harder than diamond and more flexible than rubber. It has a high degree of thermal and electrical conductivity.
No wonder there is now a lot of research into the application of graphene. The promises are promising. It would make the Internet 100 times faster or a camera sensor 1,000 times more sensitive.
Borophene
The discovery of graphene led to more interest in other two-dimensional materials. One interesting candidate is borophene, a single layer of boron atoms that can form different crystal structures. This material, first synthesized in 2015, appears to be stronger and more flexible than graphene and has excellent conductive properties.
The material seems promising in several areas:
- as anode material in more powerful lithium-ion batteries;
- as a catalyst for various chemical reactions;
- as a sensor for detecting atoms and molecules;
- as a medium for hydrogen storage;
As with graphene, there are still plenty of challenges, such as how fabs can scale up production and how to protect the material from oxidation.
Combination with artificial intelligence
An interesting boost for materials science is artificial intelligence. For example, in late 2024, the research team at DeepMind (part of Alphabet, Google’s parent company) announced that they had developed the model GNoMe. This stands for Graph Networks for Materials Exploration. This AI model developed more than 2.2 million new materials. Of these materials, about 380,000 are considered stable enough for further scientific research.
Nanotechnology
A mix between materials science and biotechnology is nanotechnology. Nanotechnology is about manipulating and controlling matter at the atomic and molecular scale. Developments in nanotechnology can lead to new materials and breakthroughs in biotechnology, such as targeted drug delivery into the human body.
2. 3D printing
A 3D printer can print materials in predefined shapes. As far as those materials are concerned, they are now mainly plastics, but you can also print stone, wood and fabrics today.
You can make the comparison with the distribution of digital files such as music and movies.
‘With a downloaded STL file, your 3D printer can create a piece of furniture conceived by someone on the other side of the world.’
This is the democratization of products: you download a design you like of whatever object and print it out at a nearby 3D printer. When this technology emerged, that was also the picture: there would be such printers in every home or else in shopping malls. In the end, this has not (yet) come to pass.
Medical science is interested in applying this method to tissues and possibly, in the future, organs. This is 3D bioprinting.
3. Space
A lot is happening in the field of space exploration. This is mainly due to the emergence of commercial providers such as SpaceX and Blue Origin.
Some interesting developments:
- In September 2025, Artemis 2 is scheduled, the first manned lunar mission within the Artemis program. The last manned lunar mission was Apollo 17, which took place in December 1972.
- The company AstroForge focuses on mining in space. In 2025, they want to dock to a metal-rich asteroid with mission Vestra. The next step is to actually mine metals on asteroids.
- The company Orbital Assembly Corporation plans to open a space hotel in 2027 that can accommodate 400 guests.
- Around 2027, SpaceX plans to send the first unmanned missions to Mars.

Extra: what are 3 key features of technological development.
Features
Three characteristics of technological development are exponential change, recombination and recursivity.
Exponential change
The basis of exponential change is Moore’s Law. This theory means that the processor speed on a chip you can buy for $1,000 doubles every 18 to 24 months. It applies not only to transistors in an integrated circuit, but also to computing power, storage capacity and genome sequencing.
Ray Kurzweil calls this “the law of accelerating returns. At first this does not seem spectacular, but over time each doubling is a huge jump.
The problem is that it is very difficult for the human brain to contain an exponential jump. We are used to linear thinking. We expect the technology we have now to get better and faster at the same rate it developed before this.
There are well-known examples to illustrate this.
- Drops of water in stadium. Every minute a drop of water falls in a stadium. The next minute, two drops fall. The next minute four drops, and so on. After 43 minutes, the stadium is 7% full. How long will it take before the stadium is completely full? Answer: only 6 minutes later!
- Grains of rice on a chess board. A nice riddle is about an Indian king who agrees to play a chess match against a mathematician. The stakes are one grain of rice on the first square, two on the second, four on third, and so on. Only when the king loses does he find out that his debt is much more than the entire world’s rice supply.
Recombination & recursivity
Besides exponential growth, recombination and recursivity are important aspects. Recombination stands for cross-pollination: combining different developments. For example, advances in biotechnology are achieved through combinations in artificial intelligence, big data and (biological) research.
Another key feature is recursivity. These are systems that can update and upgrade themselves, like robots that can reprogram themselves to handle new tasks each time. Examples in our lives: operating systems updating themselves automatically, a car getting a new update overnight or an online services like Google all testing, improving and changing daily.
PS. If you would like to hire me for a lecture or workshop on (technological) trends please contact me. Or check out the Trends 2040 page first for more information, examples and references.







Leave A Comment